When the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into effect in 2018, it completely transformed the realm of data regulation by giving EU citizens sovereignty over their personal information. Specifically, GDPR gave individuals more control over how their personal data is collected, processed, and shared by organizations.
Since then, a plethora of countries and regions have enacted data-protection laws of their own. These include Argentina, Singapore, Japan, South Korea, South Africa, China, the United Kingdom, Canada, Brazil, and a handful of US states (most notably California). Others in the process of adding such laws and regulations include Chile, Colombia, Taiwan, and Thailand.
Privacy Management
This trend has led to the emergence of privacy management as a growing concern for large and medium-sized organizations.
The collection, storage, use, and disclosure of personal data all come with risk. Privacy management helps organizations identify and manage those risks with a set of policies, procedures, and practices that organizations use to ensure (1) the protection of personal information and (2) compliance with applicable privacy laws and regulations.
The patchwork of privacy laws and regulations, varying from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, means there is no single governing body for privacy management. This creates challenges for organizations as they seek to balance compliance efforts with the need to manage other business operations as efficiently as possible.
Personal Information Management Systems
A personal information management system (PIMS) is a set of tools, techniques, and procedures used to manage personal information. It is designed to help individual data subjects manage their digital and physical information efficiently and effectively—ensuring that it is organized, secure, and easily accessible when needed. This enables them to decide how their data is collected, used, shared, and stored.
A PIMS typically includes a range of tools—data organization software, password managers, backup solutions, encryption tools, etc.—to empower individuals in categorizing and organizing their data, keeping track of important information, and protecting their data from unauthorized access or loss.
Benefits of ISO 27701-Based PIMS Implementation
To help organizations implement a PIMS while keeping in compliance with data-protection laws and regulations, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) drafted and released ISO 27701.
ISO 27701 provides guidelines and requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a PIMS. The standard is designed to assist organizations in establishing and maintaining an effective privacy-enhancing technology (PET) tool set that integrates privacy requirements into information-security (InfoSec) tooling.
ISO 27701 is an extension to ISO's better-known InfoSec-management standard, ISO/IEC 27001. Together, ISO 27001 and its extension 27701 provide a comprehensive framework for managing InfoSec and privacy risks—including risk assessment, risk treatment, and risk monitoring.
While organizations can implement their own policies and procedures independently, implementing a PIMS using globally recognized and accepted standards such as ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 can provide several advantages.
1. Providing clarity on roles and responsibilities
Effective implementation and execution of a privacy program requires a very clear identification of roles and responsibilities; this ensures full accountability for privacy activities within the implementing organization, compliance with privacy regulations and standards, coordination and communication among all stakeholders, and continuous improvement. By assigning specific tasks and responsibilities to individuals or teams within the implementing organization, ISO 27701 increases accountability among all stakeholders by establishing clear roles and responsibilities.
2. Demonstrated compliance with various laws and regulations
ISO 27701 is designed to align with the requirements of multiple international privacy laws and regulations (such as addressed above). It requires organizations to develop and maintain clear privacy-management policies and procedures for managing and protecting personally identifiable information (PII) in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
By implementing a PIMS based on this standard, an organization can more effectively ensure compliance with data-privacy laws and regulations while giving back to data subjects control over their data. It's also good for the organization's brand and reputation insofar as it demonstrates the organization's commitment to InfoSec and privacy.
3. Ability to manage data-privacy risks systematically
ISO 27701 provides a structured programmatic approach for managing and executing privacy programs for compliance. The key elements of this approach include:
- The establishment and maintenance of a privacy policy that defines the objectives and principles of the privacy program
- The identification of and compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations, including country-specific and regional data-protection laws and regulations
- The regular conduct of privacy risk assessments
- The provision of controls and measures for organizations to implement to address privacy risks and compliance requirements
- The requirement that organizations establish and maintain procedures for identifying, reporting, and managing privacy incidents
- The requirement to monitor and evaluate privacy programs—and take corrective measures as necessary
4. Building trust with external stakeholders
Trust is a vital factor in the development of privacy practices. Taking data-privacy regulations into account, trust refers to the fundamental principle that personal data must be processed lawfully, fairly, and in a transparent manner to ensure the protection of each data subject's rights and freedoms.
From a PIMS perspective, trust requires the following:
Employing best practices when collecting and handling user data
Using data only in accordance with the purposes for which a person has given their explicit consent for its use and processing
Storing data within contractually agreed-upon geographical boundaries
5. Integration with existing information security standards
As an extension to ISO 27001, ISO 27701 works in conjunction with most data-protection enabling/enhancing technologies. ISO 27701 includes guidelines for implementing controls surrounding data minimization, data-subject access requests, breach notification, and the management of third-party processors—with a view towards protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data.
Implementation
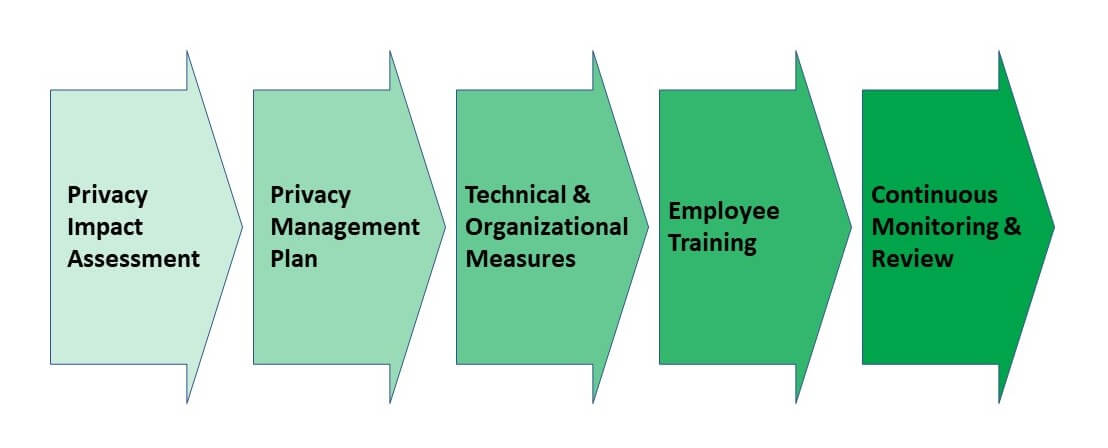
Implementing a PIMS can be a complex process. Here are a few steps enterprise-IT leaders should follow to comply with ISO 27701 as they implement a PIMS:1. Conduct a privacy-impact assessment
The first step is to conduct a privacy-impact assessment (PIA) to identify the personal data collected, processed, and stored by the organization. From an ISO 27701 perspective, a PIA must systematically examine the potential impacts that a particular processing activity may have on the privacy of individuals regarding the context, nature, purpose, and scope of the processing activity while considering the type of personal data involved.
The PIA will help identify potential privacy risks and provide a basis for developing a privacy-management plan.
2. Develop a privacy-management plan
The next step is to develop a privacy management plan—based on the results of the PIA—that includes policies and procedures for handling personal data. ISO 27701 stipulates that a privacy-management plan should include the following elements:
A privacy policy: A statement that outlines the organization's commitment to protecting personal information and the principles it will follow when processing personal information.
A privacy-risk assessment: A process for identifying and assessing privacy risks associated with the organization's processing of personal information. ISO 27701 requires organizations to conduct privacy risk assessments and implement appropriate controls to mitigate privacy risks.
Privacy controls: Measures that the organization will implement to manage privacy risks and protect personal information, including technical and organizational controls. ISO 27701 requires organizations to implement controls for managing third-party access to PII, including the assessment of third-party privacy practices and ensuring that contracts with third parties include appropriate privacy provisions.
Privacy training and awareness: A program for providing privacy training to employees and raising awareness of privacy risks within the organization.
Incident management: Procedures for managing privacy incidents, including the reporting and investigation of incidents and the implementation of corrective actions.
Monitoring and review: Processes for monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the organization's privacy-management program and making improvements as necessary.
3. Implement technical and organizational measures
Implement technical and organizational measures to protect personal data. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and other security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
4. Train your employees
As per your privacy-management plan, train your employees on the organization's privacy policies and procedures. This includes providing training on how to handle personal data, how to report privacy incidents, and how to comply with applicable privacy regulations.
5. Monitor and review PIMS effectiveness
Continuously monitor and review the impact and achievements of PIMS to ensure that it remains effective and up to date. This includes conducting periodic risk assessments, and reviewing and updating policies, processes, and procedures as necessary.
As the list of data-protection regulatory regimes continues to grow, enterprise IT leaders need to systematize their privacy-management operations to minimize risk and maximize operational efficiency. By following all of the above steps, enterprise IT leaders can implement a PIMS using ISO 27701 to manage personal data in compliance with privacy regulations—helping to protect the privacy rights of individuals.
Keep learning
Understand the newest privacy laws with this Webcast: California’s own GDPR? It’s not alone.
Take a deep dive into the new privacy laws with TechBeacon's Guide to GDPR and CCPA.
- Get up to speed on cloud security and privacy and selecting the right encryption and key management with TechBeacon's Guide.